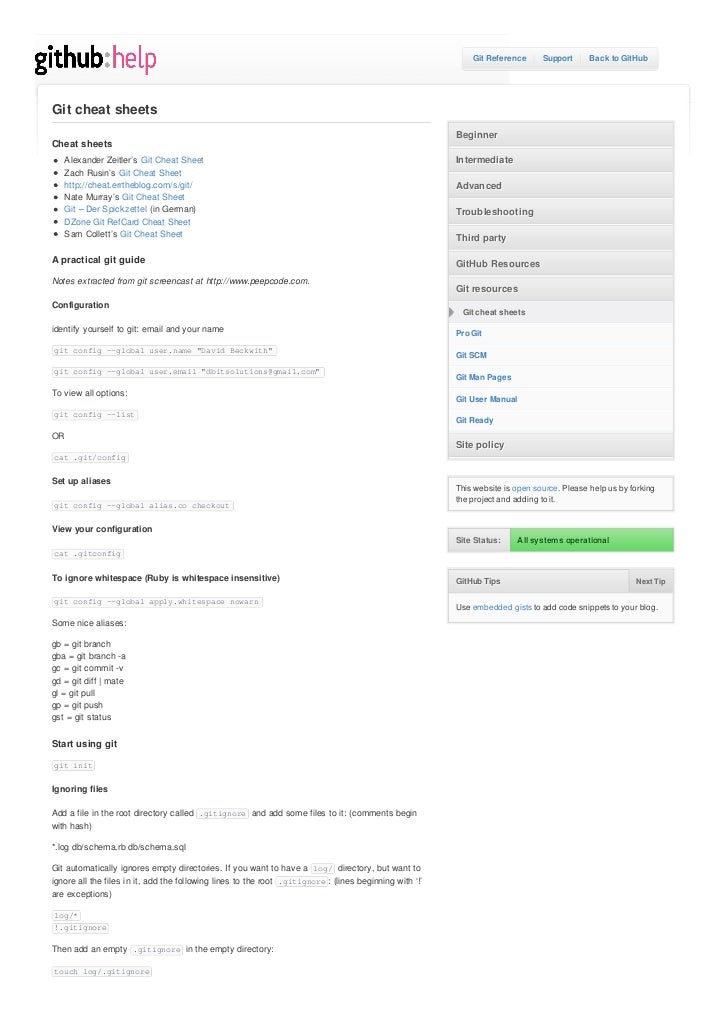
Github Cheat Sheet
This is just stuff that I have put down that I find I use a lot of the time for my own reference.
Latest changes from repo to your machine
- Cheat Sheet: 10 GitHub Security Best Practices www.snyk.io Never store credentials as code/config in GitHub. Some good practices: You should include a SECURITY.md file that highlights security related information for your project. This should contain: Disclosure policy. Define the procedure for what a reporter who finds a security issue.
- For (let key, value of Object.entries(object1)) returns array of object's keys and values: key, value MDN.
$ git branch -d branch-name Deletes the specified branch Git is the open source distributed version control system that facilitates GitHub activities on your laptop or desktop. This cheat sheet summarizes commonly used Git command line instructions for quick reference. INSTALL GIT GitHub provides desktop clients that include a graphical user.
Add tracking information to your work
Assuming that you are working on the master branch then
You can set it to whatever branch you want to track changes for
This will mean you can just do git pull and the latest changes will be pulled to your origin
What branch?
$ git branch shows what branch you're on
$ git branch -r shows remote branches
$ git branch -a shows all branches
Create a PR [Pull Request]
Fork other users repo in GitHub, then clone to your machine.
Add the remote repo
Create your branch
Check it out
If adding a folder use.
Make your commit and push to your new branch.
Manage the rest of the PR via GitHub
Check remotes
Sync a remote fork on your machine
First configure the local to point to the remote upstream
You then use git merge to update any branch on the upstream repository:

Sync a remote fork on Github

- Open your fork on GitHub.
- Click on Pull Requests.
- Click on New Pull Request. By default, GitHub will compare the original with your fork, and there shouldn’t be anything to compare if you didn’t make any changes.
- Click on Try
switching the base. Now GitHub will compare your fork with the original, and you should see all the latest changes. - Click on Click to create a pull request for this comparison and assign a predictable name to your pull request (e.g., Update from original).
- Click on Send pull request.
- Scroll down and click Merge pull request and finally Confirm merge. If your fork didn’t have any changes, you will be able to merge it automatically.
2fa
Git Cheat Sheet
Using two factor authentication? Then use the following so you're not adding in your auth token each time you want to push your code.
Change origin url
If you want to change the origin url you can use the set-url command
Via terminal navigate to your code folder.
Add your files.
Adding a folder use the following syntax or it'll get added as a BLOB.
Commit to local repo.
To add your files to the remote repo, first add your remote repo
Delete local branch
Merge two repos
If you want to merge project-a into project-b:
Stop tracking a file
If you have .env files that are tracked by Git and want to ignore them so your API keys don't get added to GitHub use:
Start tracking a previously un-tracked file
Cloning a repo from someone else's GitHub and pushing it to a repo on my GitHub
So you make a clone, make some changes then realise that you need to add it to your GitHub account before making a pull
You just need to set the origin to yours then add the upstream as the original origin make sense?

So change origin to yours:
Then add upsrtream as theirs:
Github Commands Cheat Sheet
Now it should look something like this:
Clone a repo and give it a different name
Using Husky?
If you are pushing right after a commit, you can use $ git push --no-verify to avoid running all the tests again.
If you make a trivial change and want to commit $ git commit -m 'some detailed message' --no-verify will skip your precommit and prepush scripts.
How to read last commit comment?
$ git show is the fastest to type, but shows you the diff as well.
$ git log -1 is fast and simple.
$ git log -1 --pretty=%B if you need just the commit message and nothing else.
Remove commit from pull request
Read this for more detail on how to revert.
This was the simplest approach I found:
Rather than use the last part I unstaged the changes in VSCode which I think did the same thing.
Show .gitconfig details
If you want to rename a branch while pointed to any branch, do:
If you want to rename the current branch, you can do:
Github Cheat Sheet Pdf
A way to remember this, is -m is for 'move' (or mv), which is how you rename files.
